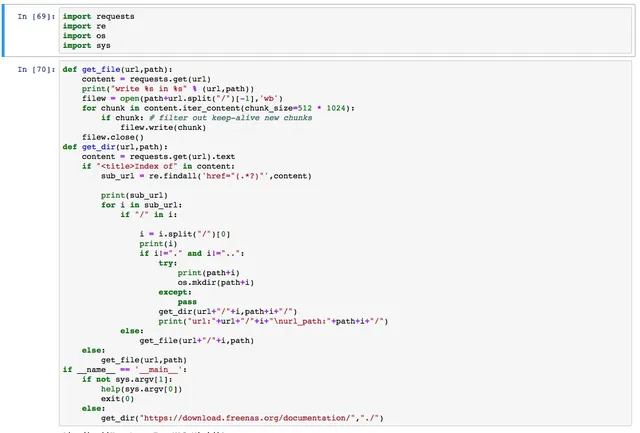
The network module in python3 is much more convenient compared to python2. The requests package combines several python2 packages. This article explains the usage of requests with examples, serving as a review and future reference.
requests is not installed by default in python, you can install it with pip install requests. Below are usage examples of the requests module.
GET fetch webpage content
import requests
r = requests.get("https://www.bobobk.com/vip_parse")
print("Status code:n%d" % r.status_code) # status code
print(r.headers['content-type']) # header encoding
print("Webpage content:n%s" % r.content.decode("utf8")[:100]) # content returns raw bytes, decoded here as utf8
print("Webpage content:n%s" % r.text[:100]) # text returns str type
What if the URL has parameters? It’s very simple. For convenience, requests lets you pass parameters using params={"url":"https://www.bobobk.com","id":"1"}
Of course, you can still write a long URL manually if you want, no problem.
POST data
Posting data is also very simple, use the data parameter with a dictionary containing the data to post.
import requests
r = requests.post('https://httpbin.org/post', data = {'key':'value'})
Add headers
Sometimes websites restrict user agents (UA). The default UA used by requests includes “requests” in it, so if you want to modify headers, do this:
import requests
headers = {'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (X11; U; Linux x86_64; zh-CN; rv:1.9.2.10) Gecko/20100922 Ubuntu/10.10 (maverick) Firefox/3.6.10'}
url="https://httpbin.org/get"
r = requests.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=5)
# or set timeout for delay
Basic authentication
If the website uses basic authentication, just add the auth parameter.
r = requests.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=5, auth=HTTPBasicAuth('username', 'password'))
# Since HTTPBasicAuth is common, python allows you to pass a tuple directly:
r = requests.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=5, auth=('username', 'password'))
GET download file
r = requests.get('https://www.bobobk.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/wizard.webp')
f = open('download.webp', 'wb')
for chunk in r.iter_content(chunk_size=512 * 1024):
if chunk:
f.write(chunk)
f.close()
This method supports downloading large files.
POST file
You can also post files directly by adding the files parameter, like this:
url = 'https://httpbin.org/post'
files = {'file': ('myfile.xls', open('myfile.xls', 'rb'), 'application/vnd.ms-excel', {'Expires': '0'})}
r = requests.post(url, files=files)
Using COOKIE
Just specify the cookies parameter directly:
url = 'https://httpbin.org/cookies'
r = requests.get(url, cookies={"username":"bobobk"})
# If the webpage response contains cookies, you can also easily get cookies:
r.cookies