Using Matplotlib's fill_between for Area Filling in Python
Data visualization is a crucial part of data analysis, and the fill_between() function in the Matplotlib library can significantly enhance chart expressiveness. This tutorial will demonstrate three practical methods for area filling.
Data Preparation
First, let’s create a sine wave as our base data:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
n = 1024
x = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, n, endpoint=True)
y = np.sin(2 * x)
plt.plot(x, y, color='blue', alpha=1.00)
plt.savefig("sine_wave.png", dpi=200)
plt.close()
The resulting sine function plot is:
Matplotlib Fill Below
To fill with color using fill_between, since the sine function’s range is 0-1, with 0 at its lowest point, the y2 parameter for filling downwards will be 0, representing the line y=0.
plt.plot(x, y, color='blue', alpha=1.00)
plt.fill_between(x, y, 0, color='blue', alpha=.1)
plt.savefig("sin_fill_below.png",dpi=200)
plt.close()
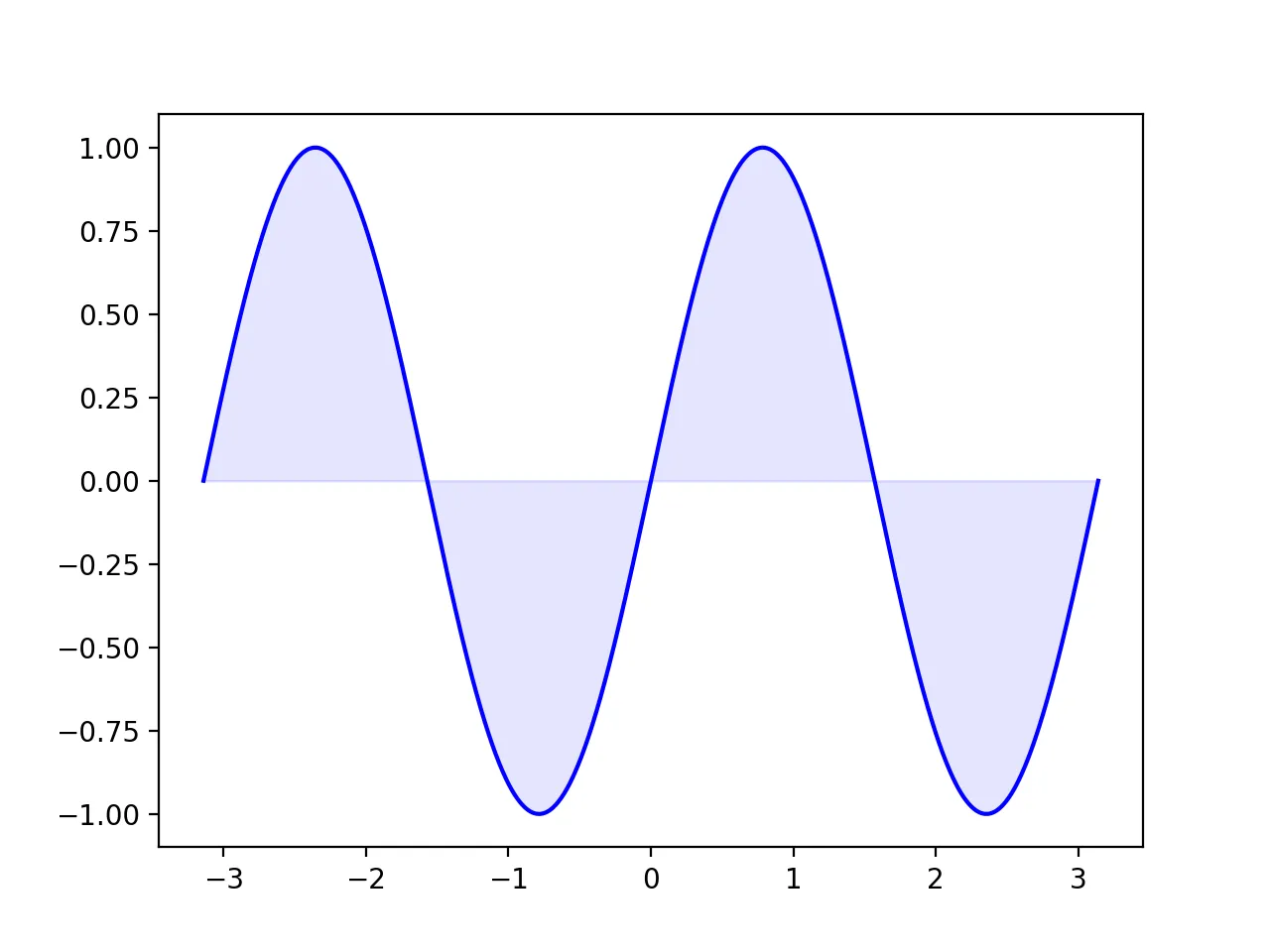 Key parameter explanations:
Key parameter explanations:
x: X-axis valuesy: Main curve values0: Fills down to y=0alpha: Controls transparency (0-1)
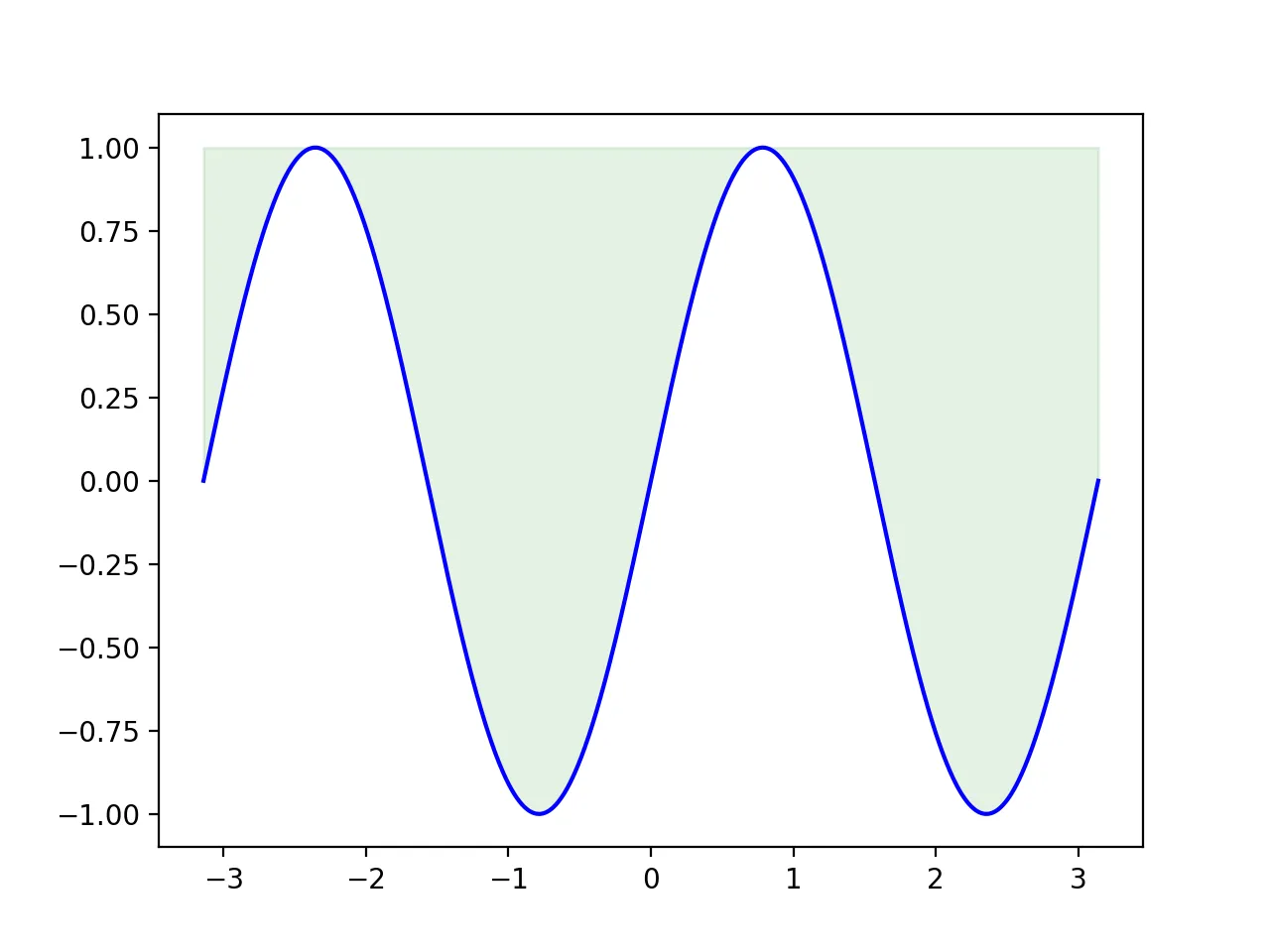
Matplotlib Fill Above
To fill with color using fill_between, the y2 parameter for filling upwards will be 1, representing the line y=1.
plt.plot(x, y, color='blue', alpha=1.00)
plt.fill_between(x, y, 1, color='green', alpha=.1)
plt.savefig("sin_fill_above.png",dpi=200)
plt.close()
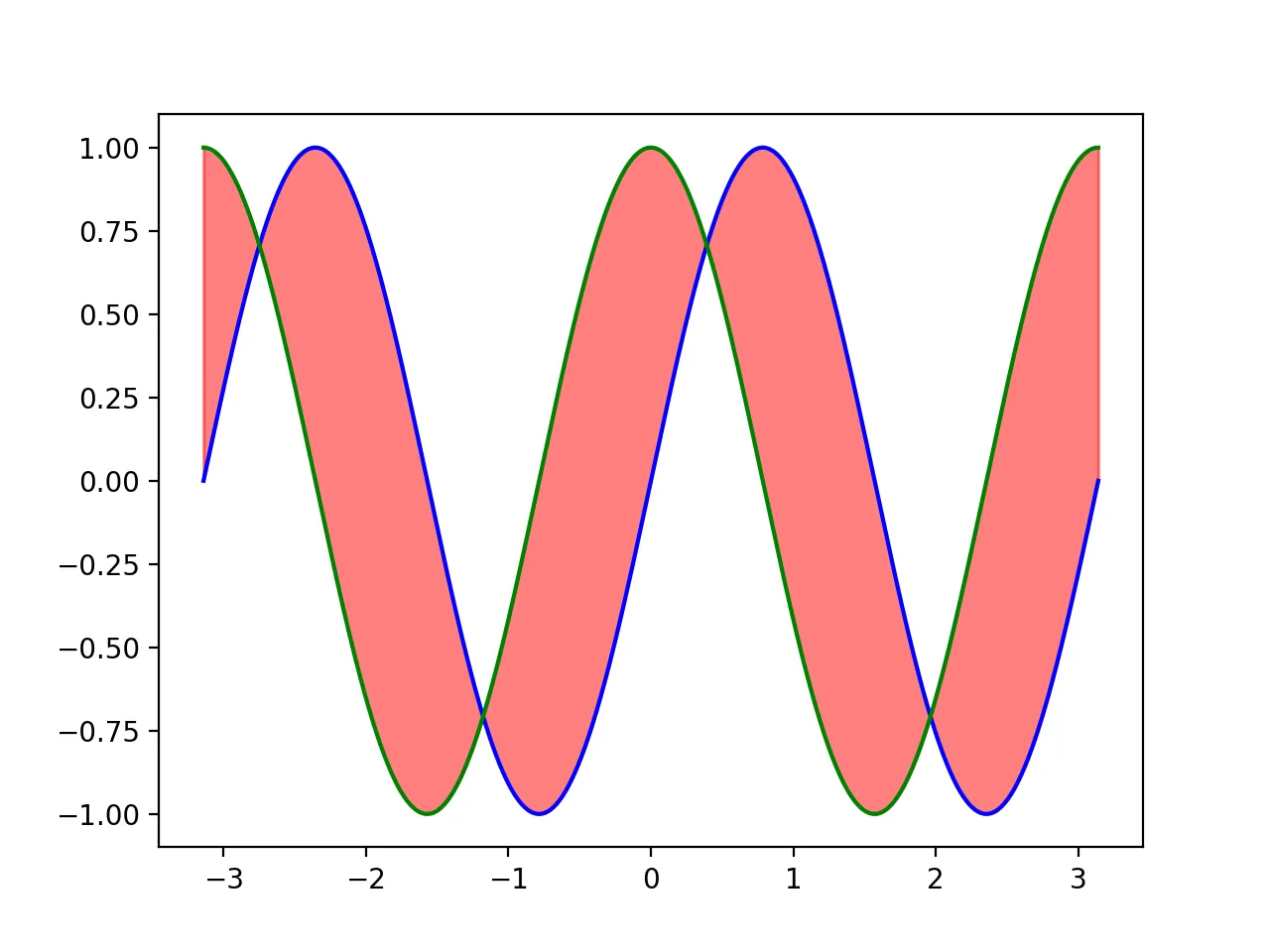
Matplotlib Fill Between Two Lines
Similarly, the difference lies in changing fill_between to the corresponding values for the lines. Here, we use cosine as the second line and fill the area between sine and cosine with red. The code is as follows:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
# Data Generation
n = 1024
x = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, n, endpoint=True)
y = np.sin(2 * x)
y2 = np.cos(2*x)
# Plotting
plt.plot(x, y, color='blue', alpha=1.00)
plt.plot(x, y2, color='green', alpha=1.00)
plt.fill_between(x, y, y2, color='red', alpha=0.5)
plt.savefig("sin_cos_fill.png",dpi=200)
The resulting graph is:
Practical Application Scenarios
The fill_between function is particularly suitable for:
- Highlighting confidence intervals
- Visualizing data ranges
- Comparing time series data
- Creating stacked area charts
Summary
Mastering Matplotlib’s fill_between() function can significantly enhance Python data visualization effects. Whether for scientific plotting, business dashboards, or exploratory data analysis, these techniques can make your charts more informative and visually appealing.
- 原文作者:春江暮客
- 原文链接:https://www.bobobk.com/en/748.html
- 版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可,非商业转载请注明出处(作者,原文链接),商业转载请联系作者获得授权。